Adventure tourism is defined as the movement of the people from one to another place outside their comfort zone for exploration or travel to remote areas, exotic and possibly hostile areas. Adventure tourism is a type of tourism in which tourist do some adventures activities like as skydiving, hill climbing, scuba diving.
Adventure tourism is very popular among young age tourists. Adventure tourism gains much of its excitement by allowing the tourists to step outside their comfort zone. This may be from experiencing cultural shock or through the performance of acts, that required some degree of risk (real or perceived) and physical danger.
Adventure travel is a leisure activity that takes place in an unusual, exotic, remote or wilderness destination. It tends to be associated with high levels of activity by the participant, most of it outdoors. Adventure travelers expect to experience various level of risk, excitement, and tranquility and be personally tested. In particular, they are explorers of unspoiled, exotic parts of the planet and also seek personal challenges.
The main factor distinguishing adventure tourism from all other forms of tourism is the planning and preparation involved.
Definitions of Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism is a new concept in the tourism industry. Tourism industry adopted adventure tourism, but there is not any specific definition of adventure tourism. Most commentators concur that adventure tourism is a niche sector of the tourism industry, but there are many other niche sectors in tourism which have same characteristics that overlap with adventure tourism such as ecotourism, activity tourism or adventure travel.
One of them can confuse. Adventure tourism is a complicated and ambiguous topic. Some important definitions of adventure tourism are following as:
According to the Adventure Travel Trade Association, “adventure tourism is a tourist activity that includes physical activity, cultural exchange, or activities in nature.
According to Muller and Cleaver, “Adventure tourism is characterized by its ability to provide the tourist with relatively high levels of sensory stimulation, usually achieved by including physically challenging experiential components with the tourist experience.”
Canadian Tourism Commission in 1995 defines adventure tourism as, “an outdoor leisure activity that takes place in an unusual, exotic, remote or wilderness destination, involves some form of unconventional means of transportation, and tends to be associated with low or high levels of activity.”
According to Sung et al, “adventure tourism is the sum of the phenomena and relationships arising from the interactions of adventure touristic activities with the natural environment away from the participant’s usual place of residence area and containing elements of risk in which the outcome is influenced by the participation, setting, and the organizer of the tourist’s experience.”
According to UNWTO, ” adventure tourism can be domestic or international, and like all travel, it must include an overnight stay, but not last longer than one year.”
History of Adventure Tourism
Humans are traveling from ancient time for the searching for foods, and for many survival reasons. Humans have been engaging in adventurous travel for hundreds of year via exploration. People traveled in ancient time for exploration of sea roots, new destination, or even a new country.
However, commercial adventure travel is a new phenomenon, in which travelers hire a professional guide to provide a range of technical support and equipment, as well as cultural and nature interpretation.
In the mid-1800s, adventurers began to push the limits of mountain climbing and river rafting, with the first ascent of the Matterhorn in 1865 and decent of the Colorado River in 1869. Shortly thereafter, two key institutions were formed. The National Geographic Society and Explorers Club. These institutions are supporting adventures tourism continuously.
In the mid- 1950s, many first ascents and descents attracted global attention and inspired many people to attempt their own expeditions. Maurice Herzog’s ascent of Annapurna in 1950, Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzig Norgay’s ascent of Mount Everest, and other successes were hailed in the media around the world. This was the takeoff of modern adventure tourism.
Today, adventure tourism is a vibrant, dynamic, and fast-changing sector with new variants routinely added into the possible experience.
Types of Adventure Tourism
Adventure tourism has grown exponentially all over the world in recent years with tourist visiting destinations previously undiscovered. This allows for a new destination to market themselves as truly unique, appealing to those traveler looking for rare, incomparable experience.
Adventure tourism includes various activities like caving, hiking, sailing, trekking etc. Adventure tourism categorized into two categories. These are following as:
- Hard Adventure
- Soft Adventure
Hard Adventure
Hard adventure refers to activities with high levels of risk, requiring intense commitment and advanced skills. Hard tourism includes the activities like climbing mountains/rock/ice, trekking, caving etc.
Hard adventure activities are highly risked in nature. Professional guide, advance level skills are required to perform these activities. Many tourists died during climbing mountains, caving every day. There is an interesting fact that is for K2, world 2nd highest mountain, for every two people who submit one dies.
Soft Adventure
Soft adventure refers to activities with a perceived risk but low levels of risk, requiring minimal commitment and beginning skills; most of these activities are led by experienced guides. Soft tourism includes the activities like backpacking, camping, hiking, kayaking etc.
Soft adventure activities are low risk in nature. These activities are led by professional guides. Soft adventure is a popular category in adventure tourism. On average, 25% trips taken from North America and Europe are soft adventure trips.
Adventure Tourism Activities
Adventure travelers are early adopters by nature, meaning they are generally more willing to try new destinations, activities, and travel products. Popular activities change rapidly, and it seems there is a new twist on an existing sport evert years.
Some activities have low risk and some have high. Adventure tourism activities are classified into two types:
- Hard Adventure Activities
- Soft Adventure Activities
Hard Adventure Activities
Hard adventure activities are highly risky and dangerous in nature. These activities are following as:
- Caving
- Mountain Climbing
- Rock Climbing
- Ice Climbing
- Trekking
- Sky Diving
Soft Adventure Activities
These activities are less dangerous and risk as compared to hard adventure activities. These activities are always lead by professional guides. These activities are following as:
- Backpacking
- Birdwatching
- Camping
- Canoeing
- Eco-tourism
- Fishing
- Hiking
- Horseback riding
- Hunting
- Kayaking/sea/whitewater
- Orienteering
- Safaris
- Scuba Diving
- Snorkeling
- Skiing
- Snowboarding
- Surfing
Adventure tourism activities sit well with the environment because the natural world provides us with the resources for many of the activities that provide risk, challenge, sensory stimulus, novelty, discovery and so on.
Characteristics and Features of Adventure Tourism
The threefold combination of activity, nature, and culture marks adventure travel as an all-round challenge. Some unique characteristics and features of adventure tourism are following as:
- Physical activity, i.e. activities involving physical exertion or psychomotor skills.
- Contact with nature, i.e. activities bringing contact with the natural world in general, or with specific wildlife.
- Contact with different cultures, i.e. people, faith, lifestyles
- Journeys, i.e. vehicle-, animal-, or human-power.
- Uncertain outcomes
- Danger and risk
- Challenges
- Anticipated rewards
- Novelty
- Stimulation and excitement
- Exploration and discovery
- Contrasting emotions
Adventure Tourism Supplier
A tourism supply chain is the system of people, products, activities, and materials that get a product or service from its raw state through production and distribution to the consumer.
As with any sector, volume discounts drive the mass price point, so major retailers primarily market select trips that sell in high volume. The supply chain for these mass tourism products is often very simple, comprising only transportation and accommodation elements.
The adventure tourism supply chain is more complex. Niche products often require specializes in knowledge and operations. Adventure tourism’s supply chain linkages go very deep, and this is one of the key reasons that adventure tourism delivers greater benefits at the local level.
Supply chains vary from destination to destination. The makeup of the most involved adventure supply chain is typical as follows:
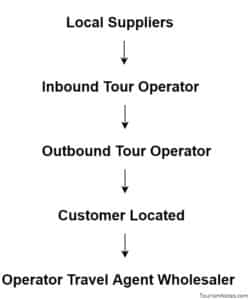
Without a proper supply chain, the tourism sector can not survive. Tourism suppliers are the backbone of the tourism industry. Adventure tourism suppliers work at a different, different level like as domestic as well international level.
Adventure Tourism Importance and Benefits
Adventure tourism is one of the fastest-growing sectors of the tourism sector, attracting high-value customers, supporting local economies, and encouraging sustainable practices.
The continued growth of this sector creates net positive impacts not only for tourism, but also for destination economies, their people, and their environment.
Some importance and benefits of adventure tourism are following as:
Employment Generation
Adventure tourism generates the jobs. Adventure tourism generates directs jobs to accommodation, transportation sector and for travel agencies or tour operators. Adventure tourism also provides the indirect job to tourism suppliers.
Adventure tourism plays an important role in the generation of employment in the economy.
Foreign Exchange
Adventure tourism attracts the foreign tourists at a large scale, as a result, it helps in foreign exchange generation.
When tourist travel to another country, they spend a large amount of money on accommodation, transportation, and shopping. Adventure tourism generates foreign exchange and supports the economy of the host country.
Economy Development
Adventure tourism helps in the development of the host country’s economy. Adventure tourism activities directly support the economy in various forms. The more tourists, more economic growth.
Support Local Communities
Adventure tourism helps in the development of infrastructure and support local communities. Adventure tourism activities directly contributed to the local economy of the communities and increase the living standards of local people.
Conservation of Natural Resources
Adventure tourism activities are nature-based activities. Leaders in the adventure tourism industry are dedicated to making this tourism segment as sustainable as possible. They help in conservation of natural resources as well as cultural.
Creating Business Opportunities
Adventure tourism activities create new business opportunities. There are companies that specialize in helping emerging adventure tourism operators market their product. Each new adventure tourism activity creates a new business opportunity.
Local and Foreign Investment
Adventure tourism creates business opportunities, as a result, it attracts the local as well as international investors. Investors invest their money in the accommodation, transportation, and into travel trade organization.
Adventure tourism plays an important role in the economy of the host country.