Sustainable tourism is the form of tourism that meets the needs of tourists, the tourism industry, and host communities today without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
According to The World Tourism Organization (WTO), sustainable tourism should:
1) Make optimal use of environmental resources that constitute a key element in tourism development, maintaining essential ecological processes and helping to conserve natural heritage and biodiversity.
2) Respect the socio-cultural authenticity of host communities, conserve their built and living cultural heritage and traditional values, and contribute to inter-cultural understanding and tolerance.
3) Ensure viable, long-term economic operations, providing socio-economic benefits to all stakeholders that are fairly distributed including stable employment and income-earning opportunities and social services to host communities, and contributing to poverty alleviation.
Definition of Sustainable Tourism
The World Tourism Organization defines sustainable tourism in the following manner:
“Sustainable tourism development meets the needs of present tourists and host regions while protecting and enhancing opportunities for the future. It is envisaged as leading to management of all resources in such a way that economic, social and aesthetic needs can be fulfilled while maintaining cultural integrity, essential ecological processes, biological diversity, and life support systems.”
While tourism is welcomed almost universally for the benefits and opportunities it creates, there is a growing recognition of the need to see tourism in its environmental context, to acknowledge that tourism and the environment are interdependent, and to work to reinforce the positive relationship between tourism, the environment and poverty reduction.
Sustainable tourism means tourism which is economically viable but does not destroy the resources on which the future of tourism will depend, notably the physical environment and the social fabric of the host community.
According to Richards, “Sustainable tourism is tourism which develops as quickly as possible, taking account of current accommodation capacity, the local population, and the environment. The development of tourism and new investment in the tourism sector should not detract from tourism itself. New tourism facilities should be integrated with the environment.”
Butler defines environmentally sustainable tourism as, “tourism which is developed and maintained in an area (community, environment) in such a manner and at such a scale that it remains viable over an infinite period and does not degrade or alter the environment (human and physical) in which it exists to such a degree that it prohibits the successful development and well being of other activities and processes.”

Sustainable Tourism Development
The World Commission on Environment and Development (The Brundtland Commission) brought the term ‘sustainable tourism development’ into common use in its seminal report (1987) called ‘Our Common Future.’
“Sustainable Development is the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
The definition has within it two concepts:
- The concept of ‘needs’, especially the needs of the poor.
- Ability to meet the present and future needs.
Basically, when we talk about sustainable development, the easiest definition is what we, the present generation, have inherited a certain amount of ecology and environment surrounding in terms of land, water, and air; when we leave it to the next generation, we should leave it at least in the same condition, of not in a better condition than what we inherited. This is the sum and substance if sustainable development, putting it in elementary terms.”
Need for Sustainable Tourism Development
Until the beginning of last decade tourism was seen as a profitable sector of business with no obvious constraints to growth, few barriers to entry to the market, an almost, universal welcome from governments and, for the most part, entailing few effective regulatory requirements to take the environment into account.
Commercial organizations, large and small, act on the Dawkin’s principle of self-interest. They do not make significant changes to the way they do business, which could be because of exhortations or out of good intentions, except in response to the pressure of external factors that cannot be avoided or to seize a competitive advantage.
International tourism has brought in a phase in which the opportunities of making quick profits from exploiting what was regarded as freely available natural resources dazzled the eyes of government and businessmen, as well as many local residents.
As there are many economic, social, ecological and political limits to tourism development, sustainable strategies are necessary to eradicate these problems.
Principles of Sustainable Tourism
Tourism Concern, 1991 in association with the Worldwide Fund for Nature(WWF) gives 10 principles for sustainable tourism. These are following as:
1) Using resources sustainably. The conservation and sustainable use of resources- natural, social and cultural – is crucial and makes long-term business sense.
2) Reducing over-consumption and waste. Reduction of over-consumption and waste avoids the costs of restoring long-term environmental damage and contributes to the quality of tourism.
3) Maintaining biodiversity. Maintaining and promoting natural, social and cultural diversity is essential for long-term sustainable tourism and creates a resilient base for the industry.
4) Integrating tourism into planning. Tourism development which is integrated into a national and local strategic planning framework and which undertake environmental impact assessments increases the long-term viability of tourism.
5) Supporting local economies. Tourism that supports a wide range of local economic activities and which takes environmental costs and values into account, both protects these economies and avoids environmental damage.
6) Involving local communities. The full involvement of local communities in the tourism sector not only benefits them and the environment in general but also improves the quality of the tourism experience.
7) Consulting stakeholders and the public. Consulting between the tourism industry and local communities, organizations and institutions are essential if they are to work alongside each other and resolve potential conflicts of interest.
8) Training staff. Staff training which integrates sustainable tourism into work practices, along with recruitment of personnel at all levels, improves the quality of the tourism product.
9) Marketing tourism responsibly. Marketing that provides tourists with the full and responsible information increases respect for the natural, social and cultural environments of destination areas and enhances customer satisfaction.
10) Undertaking research. Ongoing research and monitoring by the industry using effective data collection and analysis are essential to help solve problems and to bring benefits to destinations, the industry, and consumers.
Three Dimensions of Sustainable Tourism
Tourism has environmental, economic and social impacts. Sustainable tourism is about maximizing the impacts which are positive and minimizing the negative ones.
It seems that the environmental impacts are negative, the economic effects positive, and the social impacts a combination of both. However, it is also important to recognize that there are clear links between the three aspects of tourism – the environmental, economic, and social dimensions – and these are below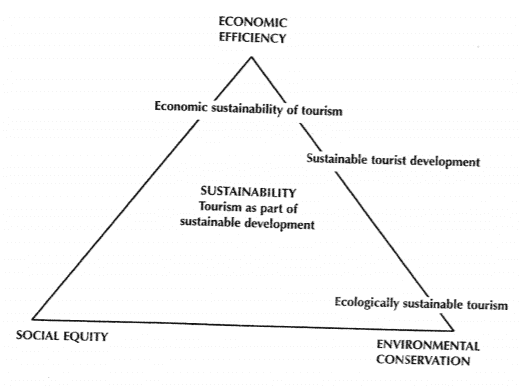 Three dimensions of sustainable tourism are:
Three dimensions of sustainable tourism are:
- Environmental
- Economic
- Social
Environmental Dimension
To many people, sustainability is about the environment, primarily the natural, physical environment, and its protection. However, there is far more to the environment than just the natural landscape.
Let us now move on to look at the five aspects of the environment:
The Natural Resources
Tourism makes use of a range of natural resources, and in many cases, the core attraction of a destination’s product may be natural resources such as clean air, land, mineral waters, and the water in lakes and seas.
The Natural Environment
There are few natural landscape or wilderness areas left in the world. Almost all natural landscapes have been affected to some extent by the actions of man through the centuries. Tourism is only one industry or activity which changes landscapes.
The natural landscape represents the core of the tourism product in many areas including natural forests, mountains, and regions which attract tourists because of their rivers and lakes.
The Farmed Environment
The farmed environment can cover a diverse range of agricultural systems including agriculture landscapes, man-made forests, and fish farms.
Wildlife
Wildlife has a number of dimensions such as land-based mammals and reptiles, flora, birds, insects, fish, and marine mammals. Tourism can clearly be very harmful to wildlife through the destruction of habitats, affecting feeding habits, disrupting breeding patterns, fires in woodlands and people picking rare plants.
The Build Environment
We also need to recognize that, in term of tourism, there are several dimensions to the built environment such as individual buildings and structures, villages and townscapes, transport infrastructure, dams, and reservoirs.
Economic Dimension
In the debate over sustainable tourism, the economic dimension is often given relatively scant attention compared to the environmental issues. Tourism is an economic phenomenon because:
- It is a major industry and foreign currency earner.
- It is the basis of the growth of many transnational corporations.
- It accounts for a significant proportion of the annual disposable income.
Economic Benefits of Tourism
Tourism contributes to the economy of a country in various ways. Economic benefits of tourism are following as:
- Job creation
- Injection of income into the local economy through the multiplier effect.
- Helping keep the local business viable.
- Infrastructure development.
- Attracts the foreign direct investments.
Economic Costs of Tourism
There are many economic benefits of tourism as well as costs. Economic costs of the tourism are following as:
- Many jobs are low paid and seasonal.
- Opportunity costs.
- Congestion.
- The need to invest in expensive infrastructure which may only be required for part of the year.
- Over-dependence on tourism makes the host economy vulnerable.
Social Dimension
The social dimension of tourism has been given less attention in the sustainable tourism debates, than the environmental impacts of tourism. This is because the socio-cultural impacts of tourism usually occur slowly over time in an unspectacular fashion. They are also largely invisible and intangible.
The social impact of tourism is usually permanent with little or no opportunity to reverse the changes once it has taken place. When the social impact of sustainable tourism has been considered the focus has normally been upon the host community.
There are a number of factors that determine whether or not the balance of socio-cultural impacts will be positive or negative in a particular location including:
- The strength and coherence of the local society and culture.
- The nature of tourism in the resort.
- The level of economic and social development of the host population in relation to the tourists.
- The measures were taken by the public sector in the destination to manage tourism in ways which minimize the socio-cultural costs of tourism.