The word hotel is derived from the French hôtel, which refers to a French version of the townhouse. The term hotel was used for the first time by the fifth Duke of Devonshire to name a lodging property in London sometime in AD 1760. Historically, in the United Kingdom, Ireland, and several other countries, a townhouse was the residence of a peer or an aristocrat in the capital of major cities. The word hotel could have also derived from the hostel, which means ‘ a place to stay for travelers‘.
A hotel is defined by the British Law as a ‘place where bonafide travelers can receive food or shelter, provided he/she is in a position to pay for it and is in a fit condition to be received‘. Hence, a hotel must provide food (and beverage) and lodging to a traveler on payment, but the hotel has the right to refuse if the traveler is not presentable (either drunk, or disorderly, or unkempt) or is not in a position to pay for the services.
Alternatively, a hotel may be defined as ‘an establishment whose primary business is to provide lodging facilities to a genuine traveler along with food, beverage, and sometimes recreational facilities too on the chargeable basis‘. Though there are other establishments such as hospitals, college hostels, prisons, and sanatoriums, which offer accommodation, they do not qualify as hotels, since they do not cater to the specific needs of the traveler.
A hotel is an establishment that provides paid accommodation, generally for a short duration of stay. Hotels often provide a number of additional guest services, such as restaurants, bars, swimming pools, healthcare, retail shops; business facilities like conference halls, banquet halls, boardrooms; and space for private parties like birthdays, marriages, kitty parties, etc.
Most of the modern hotels nowadays provide the basic facilities in a room- a bed, a cupboard, a small table, weather control (air conditioner or heater), and a bathroom- along with other feature like a telephone with STD/ISD facilities, a television set with cable channel, broadband internet connectivity.
There might also be a mini-bar containing snacks and drinks (the consumption of the same is added to the guest’s bill), and tea and coffee making unit having an electric kettle, cups, spoons, and sachets containing instant coffee, tea bags, sugar, and creamer.
History of Hotels
The invention of currency and wheels sometime in the 5th century BC are regarded as the two main factors that led to the emergence of inn-keeping and hospitality as a commercial activity. While Europe can safely be regarded as the cradle of the organized hotel business, it is in the American continent that one sees the evolution of the modern hotel industry over the past century.
From the rudimentary ancient inns to the present day state-of-art establishment that provides everything under the sun of the modern traveler, the hotel industry has come a long way. The origin and growth of the hotel industry can be broadly studied under the following periods:
- Ancient Era
- Grand Tour
- Modern Era
Ancient Era
The earliest recorded evidence of the hospitality facilities in Europe dates back to 500 BC. An ancient city, such as Corinth in Greece, had a substantial number of establishments that offered food and drink as well as beds to the traveler. The inns of the biblical era were of the primitive type, offering a cot or bench in the corner of a room and, at times, even a stable. Travelers used to stay in a large hall. Privacy and personal sanitation were non-existent.
In the 3rd century AD, numerous lodging premises mushroomed along with the extensive network of brick-paved roads throughout Europe and minor Asin (part of Asia adjoining Europe). The lodging hotels were known as mansions during that time.
These conditions prevailed for several hundred years, until the Industrial Revolution in England led to the development of railways and steamship, making traveling more efficient, comfortable, and faster. The Industrial Revolution also brought about a shift in the focus of travel that becomes more business-oriented than educational or social.
The lead-in organized hotel-keeping, as we see it today, was taken by the emerging nations of Europe, especially Switzerland. The early establishment was mainly patronized by the aristocracy and took shape in chalets (small cottages) and small hotels that provided a variety of services. Between 1750 and 1825, inns in Britain gained the reputation of being the finest hospitality establishments.
Grand Tour
The second half of the eighteenth century, prior to the French Revolution (1780-990, is referred as the ‘golden era of travel‘ as the popularity of the ‘Grand Tour‘ gave a big push to the hotel industry. In those days, a Grand Tour of the European continent constituted as an indispensable element of the education of scions of wealthy families in Britain.
As this tour often lasted several years, it was a good business opportunity for the people in prominent cities of France, Italy, Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Ireland to establish lodging, transportation, and recreation facilities. Far-sighted entrepreneurs, who smelt money in the exercise, developed the skills of the hospitality and pioneered the modern hotel industry.
Prominent among the hotels that emerged during the period were Dolder Grand in Zurich, Imperia in Vienna, the Jahreszeiten in Hamburg, and Des Bergues in Geneva. In 1841, a simple cabinet marker, Thomas Cook organized a rail tour from Leicester to Loughborough and immortalized himself as the world’s first tour operator.
Modern Era
The improvisation in the mode of transport made journeys safer, easier, and faster, enable economical as well as frequent mass movement. The introduction of Funiculars (the ropeway) made high altitude mountains accessible, leading to the growth of many hotels in Alpine rages. Burgenstock and Giessbach are among the hotels in Switzerland that owe, their existence to the development of the ropeways.
The two world wars, especially the second (1939-45) took their toll on the hospitality industry. The massive destruction caused by the war and the resulting economic depression proved to be a major setback to the travel business. The 1950s witnessed a slow and steady growth of travel on the European continent.
The development of aircraft and commercial passenger flight across the Atlantic stimulated that across the globe, and in the process accelerated the growth of the hotel industry.
But it is the American entrepreneurs who credited with literally changing the face of the hospitality industry with their innovation and aggressive marketing. Prior to the establishment of City Hotel lodging facilities in the American continent was patterned on the European style taverns or inns.
The City Hall, however, triggered a race among American hoteliers, resulting in the construction of the large hotels. The decade of the great depression in the 1930s witnessed the liquidity of most of the hotels in America. The hotel industry streamlined with the slow and steady growth during the 1940s. The increase in automobile travel in the 1950s led to the rise of ‘motor hotels’ or motels, a new category in the hotel industry.
The motel which offered free parking facilities served as rest houses for the people traveling between two cities or tourist destination. The following decades saw the growth of motels on a large scale, and also the introduction of budget hotels that offered basic facilities at half of the rates. Gradually, with the passage of time, they evolved into countrywide and international chains.
Hotel Organisation Structure
To carry out its vision, mission, objectives, and goals, every hotel requires a formal structure known as the organization structure. The structure defines the company’s distribution of responsibilities and authority among its management staff and employees.
It establishes the manner and extent of roles, power, and responsibilities, and determines how information flows between different level of organization. This structure depends entirely on the organization’s objective and strategies chosen to achieve them.
The most common way to represent the organization structure is through an organization chat. Each hotel is different and has unique features, so the organization charts of hotels vary from each other. The organization structure depends upon the size and function of a hotel.
Some hotel may lease their outlet to another company or may employ another agency to operate restaurant or housekeeping services. In such cases, those portions will not be a part of the organization chart of the hotel. A sample organization chart of a commercial hotel is following as:
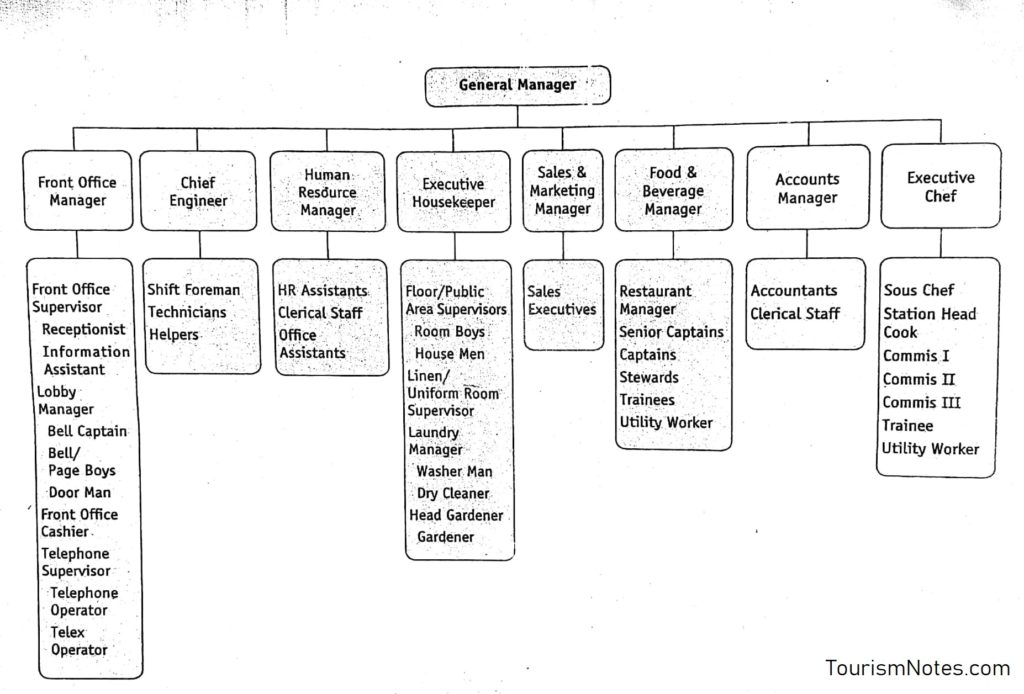
Core Areas/Departments of Hotel
The organization of a hotel today is very complex and comprises various departments. The number of departments varies from one establishment to another. All departments may have their own managers, reporting to the general manager and the assistant general manager.
Hotels departments fall under the category of either Revenue earning departments or Support departments.
Revenue earning departments are operational departments that sell services or products to the guest, thus, directly generating revenue for the hotel. These departments include front office, food and beverage, and hotel operated shops.
Support departments are the ones that help to generate revenue indirectly by playing a supporting role in the hotel’s revenue earning departments. These include human resources, maintenance, purchase, housekeeping, and so on.
The various departments in a hotel are discussed below in brief:
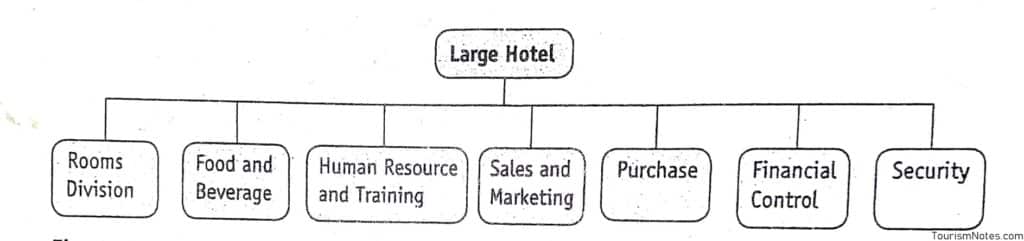
Room Division Department
In a large hotel, the housekeeping, front office, and maintenance departments come under room division. These departments together are responsible for maintaining and selling the room in a hotel. In most hotels, these are the departments that directly or indirectly generate more revenue than other departments. This is because the sale of room constitutes a minimum of 50 percent revenue of a hotel.
A hotel’s largest margin of profit comes from the room because a room, once made, can be sold over and over again. The room division is headed by the room division manager to whom the front office manager, executive housekeeper, and very often the chief engineer report.
Housekeeping Department
The housekeeping department is responsible for the cleanliness and upkeep of the front of the house areas as well as the back of the house areas so that they appear as fresh and aesthetically appealing as on the first day when hotel property opened for business. This department is headed by the executive housekeeper or, in chain hotels, the director of housekeeping.
Front Office Department
Headed by the front office manager, the front office department is the operational department that is responsible for welcoming and registering the guests, allotting the rooms and helping the guests check out. Uniformed services like concierge and bell desk and EPBAX operators are the part of the front office department.
Maintenance Department
The maintenance department also called the engineering and maintenance department, is headed by the chief engineer or the chief maintenance officer. The department is responsible for all kinds of maintenance, repair, and engineering work on equipment, machine, fixtures, and fittings.
Food and Beverage Department
The food and beverage (F&B) department include restaurants, bars, coffee shops, banquets, room service, kitchen, and bakery. The department is headed by the F&B director. While the restaurants, bars, coffee shops, banquets, and the room may be grouped specifically under the F&B service department, headed by the F&B manager, the kitchen and bakery fall under the F&B production department, headed by the executive chef.
Human Resource Department
The human resource (HR) department or the personnel department, as it used to be called earlier – is headed by the human resource manager. Recruitments, orientation, training, employee welfare and compensation, labor laws, and safety norms for the hotels come under the purview of the HR department.
The training department is an ancillary department of the HR department. This is headed by the training manager, who takes on the specific task of orientation and training of new employees as well as existing ones.
Sales and Marketing Department
The sales and marketing department is headed by the sales and marketing manager. A large hotel may have three or more employees in this department, whereas a small hotel can do with just one employee.
The function of this department is five-fold – sales, personal relations, advertising, getting MICE (meeting, incentive, conference, and exhibition) business, and market research. All these functions lead to the common goal of selling the product of the hotel – i.e. rooms and the services of the hotel by ‘creating’ customers.
Purchase Department
The purchasing department is led by the purchase manager, who, in some properties, may report to the financial controller. The procurement of all departmental inventories is the responsibility of the purchasing department. In most hotels, the central stores are the part of purchase department.
Financial Control Department
It is also called the control department, the financial control department is headed by the financial controller, who is responsible for ratifying all the inventory items of the operational departments. Inventory control procedures are the responsibility of the department.
The financial controller, along with the general manager, is responsible for finalizing the budgets prepared by the heads of other departments. The hotel’s accounts are also maintained by the controls department. Accounting activities include making payments against invoices, billing, collecting payments, generating statements, handling bank transactions, processing employee payroll data, and preparing the hotel’s financial statements.
Security Department
It is headed by the chief security officers, the security department is responsible for safeguarding the assets, guests, and employees of the hotel. Their functions include conducting fire drills, monitoring surveillance equipment, and patrolling the property.
Types and Classification of Hotels
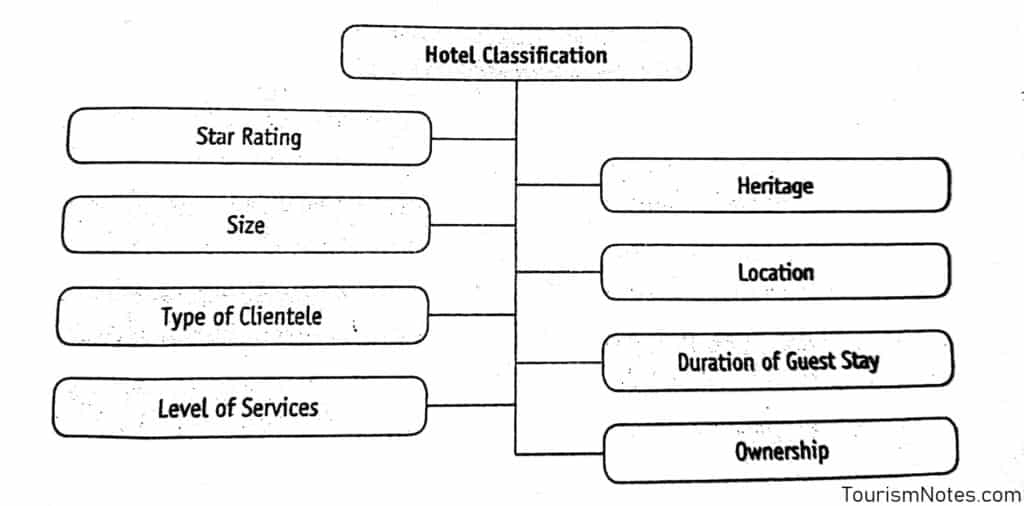
Hotels provide accommodation, along with services like food and beverages, and facilities like recreation, conference, and training arrangements, and organization of official or private parties. Each hotel has a unique feature associated with it.
The features may be its location; the number of guests room; special services such as concierge, travel assistance, and valet parking; facilities such as specialty restaurants, bars, business meeting venues, swimming pools, and so on.
The diversity in services and facilities provided by each hotel makes it quite difficult to have any single basis of classification of hotels, and if we classify them in different criteria there will be some hotels that will fall into more than one group. The criteria in which hotels are classified are following as:
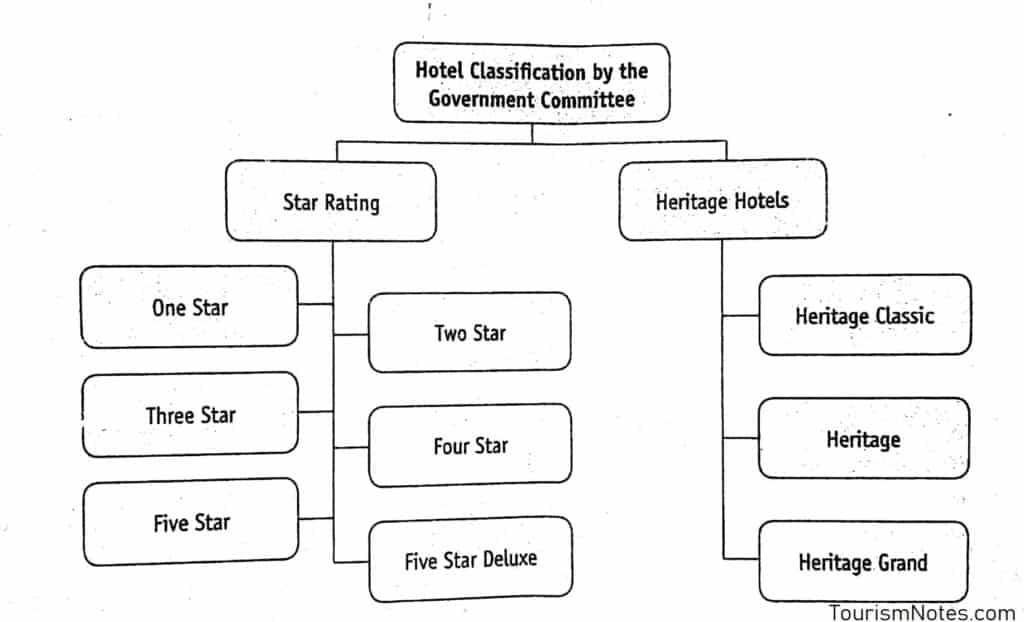
Standard Classification of Hotels
The star classification system is among the most widely accepted rating of hotels worldwide. Rating of hotels in different countries is done by the government or quasi-government sources, independent rating agencies, or sometimes the hotel operators themselves.
The brief description of the various star categories are following as:
One-star Hotels
These properties are generally small and independently owned, with a family atmosphere. There may be a limited range of facilities the meals may be fairly simple. For example, lunch may not be served or some bedrooms may not have an en-suite bath or shower.
However, maintenance, cleanliness, and comfort would be of an acceptable standard.
Two-star Hotels
In this class, hotels will typically be small to medium-sized and offer more expensive facilities than one-star hotels. Guests can expect comfortable, well equipped overnight accommodation, usually with an en-suite bath and shower.
Reception and other staff will aim for a more professional presentation that at the one-star level and will offer a wider range of straightforward services, including food and beverages.
Three-star Hotels
At this level, hotels are usually of a size to support higher staffing levels as well as significantly higher quality and range of facilities than at the lower star classifications. Reception and other public areas will be more spacious, and the restaurant will normally also cater to non-residents.
All bedrooms will have an en-suite bath and shower and will offer a good standard of comfort and equipment, such as a direct dial telephone and toiletries in the bathrooms. Besides room services, some provision for business travelers can be expected.
Four-star Hotels
Expectations of this level include a degree of luxury as well as quality in the furnishing, décor, and equipment in every area of the hotel. Bedrooms will also usually offer more space than at the lower star levels. They will be well designed with coordinated furnishing and décor.
The en-suite bathrooms will have both a bath an shower. There will be a high staff to guest ratio, with provisions of porter services, twenty-four-hour room service, and laundry and dry cleaning services. The restaurants will demonstrate a serious approach to its cuisine.
Five-star Hotels
Five-star hotels offer spacious and luxurious accommodation throughout the hotel, matching the best international standards. The interior design should impress with its quality and attention to detail, comfort, and elegance. The furnishing should be immaculate.
The services should be formal, well supervised, and flawless in its attention to the guest’s need, without being intrusive. The restaurant will demonstrate a high level of technical skill. The staff will be knowledgeable, helpful, and well versed in all aspects of customer care, combining efficiency with courtesy.
Heritage Hotels
A recent addition to the hotel industry, heritage hotels are properties set in small forts, palaces, or havelis, the mansions of erstwhile royal and aristocratic families. They have added a new dimension to cultural tourism.
In a heritage hotel, a visitor is offered rooms that have their own history, is served traditional cuisine toned down to the requirements of international palates, is entertained by folk artists, can participate in activities that allow a glimpse into the heritage of the region and can bask in an atmosphere that lives and breathes of the past.
Heritage hotels can further be divided into three types:
- Heritage
- Heritage Classis
- Heritage Grand
Classification of Hotels On the Basis of Size
The number of guest rooms in a hotel is a criterion to classify hotels. Hotels can be grouped into the following categories on the basis of the number of rooms or the size of the hotel:
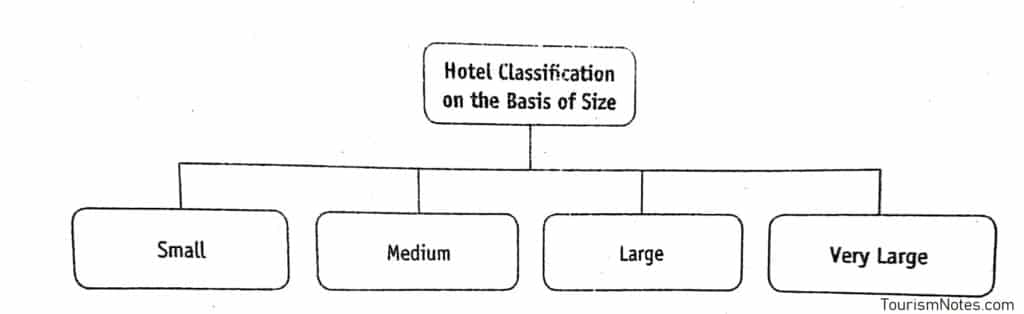
Small Hotel
In India, hotels with twenty-five or less are classified as small hotels. However, in the developed countries of Europe and America, hotels with less than 100 rooms are considered small. These hotels provide clean and comfortable accommodation but may not provide upmarket facilities, such as swimming pool, restaurant, bar etc.
Medium Hotel
Hotels with twenty-six to a hundred rooms are called medium hotels. However, in developed nations, hotels with up to 300 rooms are termed medium-sized.
Large Hotel
In India, hotels with 101 to 300 guest rooms are regarded as large hotels. Whereas, hotels with 400 to 600 rooms are termed as large hotels in the developed world.
Very Large Hotel
Hotels, with more than 300 guest rooms are known as very large hotels in our country. In developed nations, hotels with 600 to 1,000 rooms may be considered very large.
Classification of Hotels on the Basis of Location
The location of the hotel is one of the major criteria for the traveler to select and patronize a hotel. Hotels may be located in the city center, suburban areas, natural locations such as hill stations and sea beaches, near the port of entry into a country, etc. They may be classified into the following categories on the basis of their location:
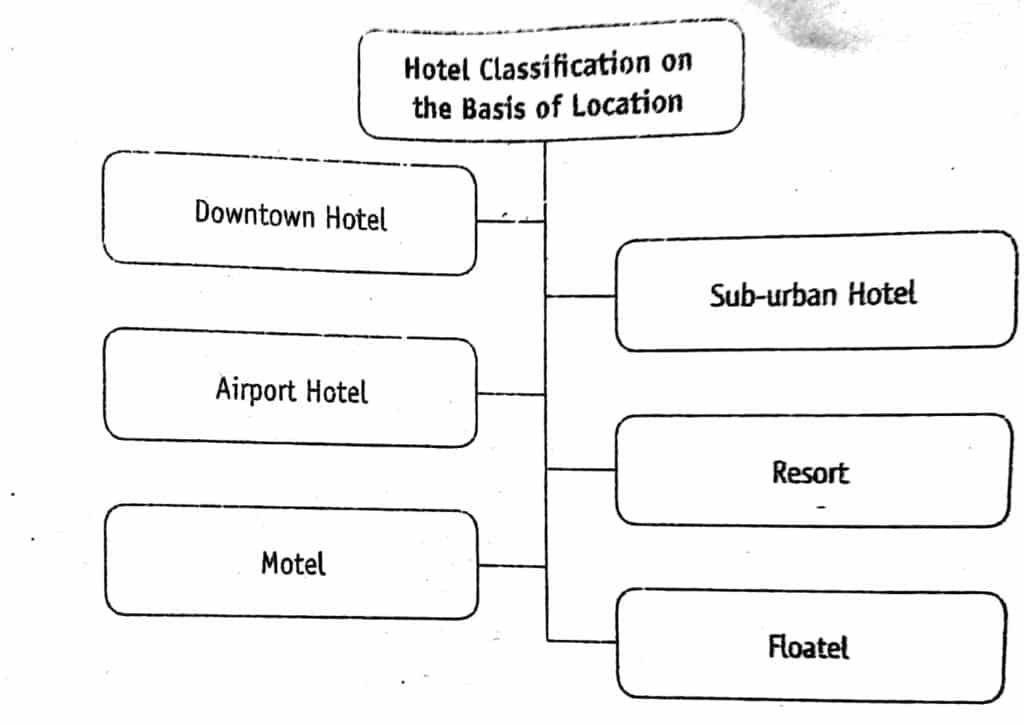
Downtown Hotel
A downtown hotel is located in the center of the city within a short distance from the business center, shopping areas, theatre, public offices, etc. The center of the city may not necessarily be the geographical center, but it refers to an area that is considered to be the commercial hub of the city.
The room rates in these hotels may be higher than similar hotels in the other areas, so as to cover the huge investment made on land. They are generally preferred by the business clients as they find it convenient to stay close to the place of their business activities.
Sub-Urban Hotel
As the land cost in the city center is higher and space is limited, some entrepreneurs build their hotel near the outskirts of the city. Providing similar facilities to the downtown hotels, these hotels are set in suburban areas and have the advantage of quieter surroundings. Such hotels are ideal for people who prefer to stay away from the hustle and bustle of a city.
The duration of the stay of guests in these hotels may be longer than the at a hotel located in the city. The room rates in such hotels are moderate and may attract the budget travelers.
Resort Hotel
Hotels that are located at a tourist destination such as hill stations, sea beaches, and countryside are referred to as resort hotels. These hotels have a very calm and natural ambiance. They are mostly away from cities and are located in the pollution-free environment. The room rates in these hotels may range from moderate to high, depending on the additional services offered.
These hotels combine stay facilities with leisure activities such as golf, summer and winter support, etc. Some of these hotels are projected as a dream destination to guests who wish to enjoy the beauty of nature and have a memorable holiday. The occupancy in the resorts is normally higher during the vacation time and weekend when guests want to take a break from their weekly routine.
Airport Hotel
Airport hotel is situated in the vicinity and other ports of entry. Offering all the services of the commercial hotel, these hotels are generally patronized by the passengers who need a stopover en-route journey.
Motel
The word ‘motel‘ is formed by the merging of two words ‘motor‘ and ‘hotel‘. They are located primarily in the highways and provide modest lodgings to highway travelers. The development of extensive road networks in the early twentieth century led to an increase in the people traveling in their own vehicles.
The phenomenon was quite common in the American European continents. The traveler who was traveling in their own vehicles needed a neat and clean accommodation for the night, so, the motel concept came into existence.
Floatel
As the name suggests, floatels are types of lodging properties that float on the water. This category consists of all lodging properties that are built on the top of rafts or semi-submersible platforms and includes cruise liners and houseboats.
Some of them provide luxurious accommodation, along with food and beverage facilities to guests.
Classification of Hotels on the Basis of Clients
The hotel caters to the need of its guests. Every individual or a group of people who patronize a hotel has a different set of requirements. While some would prefer luxurious accommodation, others would like to stay in a simple and cheap room. Some would require facilities such as meeting rooms, business centers, and conference halls if their travel is business-oriented.
Being a capital-intensive industry, the diversities in guest requirements discourage hotels from catering to all types of travelers. As a result, hotels choose to carve out a niche for themselves by catering to the needs of specific guest segments. The hotel can be classified into the following categories on the basis of its clients :
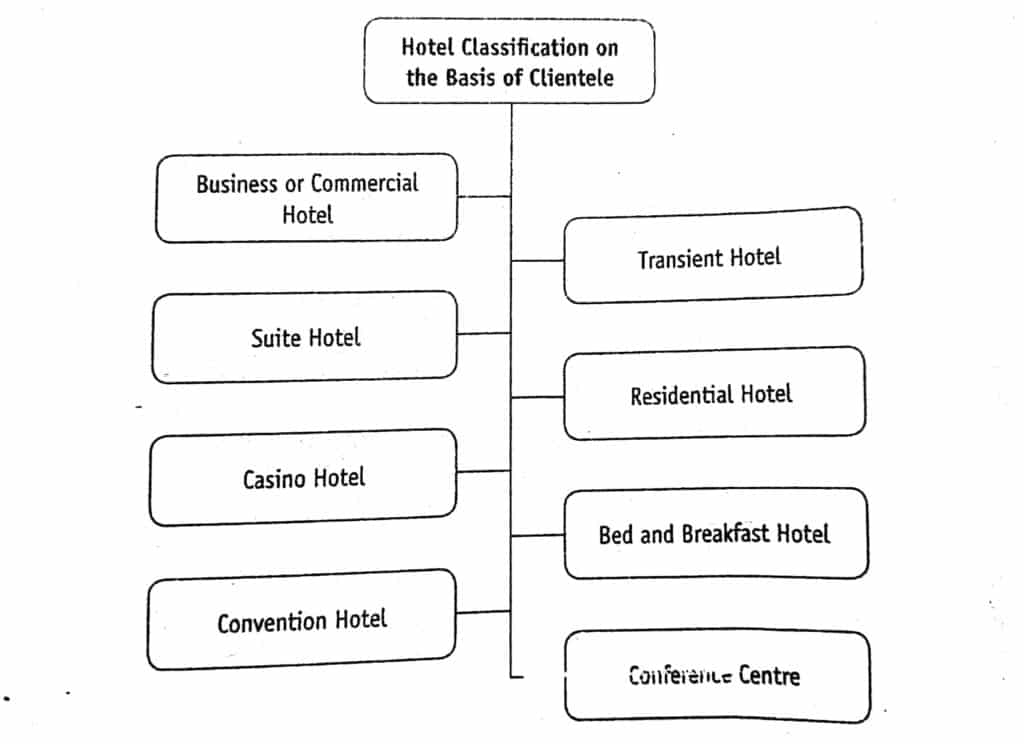
Business or Commercial Hotel
Designed to cater to the business traveler, commercial hotels are generally situated in the city center. These hotels provide high standard rooms and amenities, along with high-speed internet connectivity, business centers, and conference halls. They also provide in-house secretarial services, as well as facilities such as letter drafting, typing, fax, and photocopy of documents for the convenience of their guests.
The guest amenities at the commercial hotel may include complimentary newspapers, morning coffee, cable television, and access to channeled music and movies.
The duration of the guest’s stay is generally very short at these hotels. The occupancy level is higher during the weekdays and slightly lower during weekends. These hotels are also known as downtown hotels.
Transient Hotel
Transient hotels cater to the need of people who are on the move and need a stopover en route their journey. Located in the close proximity of ports of entry, such as seaport, airport, and major railway stations, these hotels are normally patronized by the transient traveler.
They have round the clock operational room service and coffee shop and offer all the facilities of a commercial hotel. Transient hotels are usually five-star, and their target market includes business clientele, airline passengers with overnight travel layovers or canceled flights, and airline personnel.
The occupancy rate is usually very high, sometimes more than 100 percent, as rooms can be sold more than once on a given day.
Suite Hotel
Suite Hotels provide the highest level of personalized services to guests. The guest rooms generally comprise a living area, a compact kitchenette, complete with refrigerator and a microwave, a bedroom attached with bathroom, and sometimes even a dance floor.
The facilities are highly customized and may include in-room safety locker facilities. These hotels are patronized by affluent people and tourists who are fond of luxury.
Residential Hotel
As the name suggests, residential hotels provide accommodation for a longer duration. These hotels are generally patronized by people who are on a temporary official deputation to a city where they do not have their own residential accommodation. Guest stay for a minimum period of one month and up to two years.
The services offered by these hotels are modest. The room’s configuration usually similar to that of suite hotels. Guest rooms generally include a sitting room, bathroom, and small kitchenette. They are akin to the small individual apartment.
These hotels are fully operational restaurants or a dining room for the resident guests and may provide services such as daily housekeeping, telephone, front desk, and uniformed services. The guest may choose to contract some or all the services provided by the apartment hotel. The hotel signs a lease with guest and the rent is paid either monthly or quarterly.
Bed and Breakfast Hotel
A European concept, bed, and breakfast (B&B) hotels are lodging establishments, generally operated in large family residences. These range from houses with few rooms converted into overnight facilities to small commercial building with twenty to thirty guest rooms. The owner usually lives on the premises and is responsible for serving breakfast to guests.
Guests are accommodated in bedrooms and breakfast is served in the room or sometime in the dining room. The bathrooms may be attached to the guest rooms or maybe on a sharing basis. As the tariff is generally lower than a full-service hotel at these properties, they are suitable for budget travelers.
Casino Hotel
Casino hotels provide gambling facilities, such as Luxor Hotel and Casino in Las Vegas. These hotels attract the clients by promoting gambling, arranging extravagant floor shows, and some may provide charter flight services to its clients. They have state-of-the-art gambling facilities, along with the especially restaurant, bars, round the clock room service, well appointed and furnished rooms for its guests.
Nowadays, these hotels are also attracting the MICE (meeting, incentives, conferences, and exhibitions) segment. The casinos of Las Vegas, USA are among the most famous casinos in the world.
Conference Centers
The word conference means ‘ a meeting, sometimes lasting for several days, in which people with a common interest participate in discussions or listen to lectures to obtained information‘. Thus, a conference center is a hotel which caters to the needs of a conference delegation.
These hotels provide rooms to delegates of conferences; a conference hall with the desired seating configuration for the meetings; food and beverage requirement during and after the conference; and other requirements, such as a flip chart, whiteboard with markers, overhead projector, television, VCR/VCD/DVD player, slide projector, LCD projector with screen, computer, and public address system.
These are large hotels, having more than 400 guest rooms. The services provided are the highest standard. Normally, conferences are charged as packages, which include accommodation and meeting facilities.
Convention Hotels
The convention is defined as ‘a formal assembly or meeting of members, representatives, or delegates of a group for general agreement on or acceptance of certain practices or attitudes‘. This type of meeting involves a large number of participants. The hotel catering to the needs of this segment is known as convention hotels.
These hotels may have more than 2,000 rooms to accommodate a large number of delegates. They are equipped with state-of-art convention centers with all the required facilities, such as seating configuration, audiovisual equipment, and public address systems to meet the demands of a convention.
Classification of Hotels on the Basis of Duration of Guest Stay
On the basis of the duration of the guest stay, hotels may be classified into the following categories:
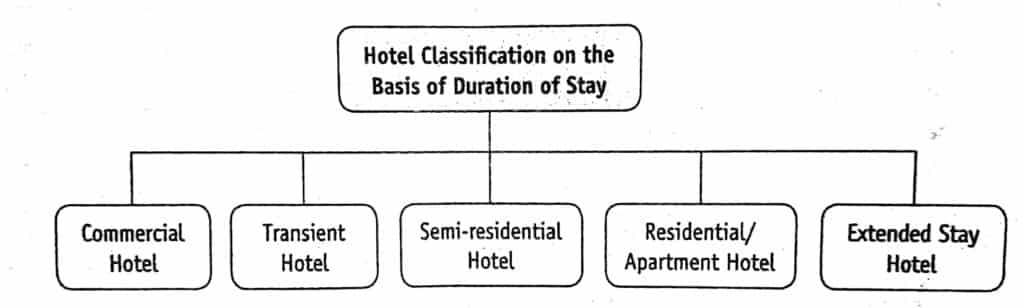
Commercial Hotel
The duration of guest stay in these hotels is short, ranging from a few days to a week.
Transient Hotel
Mostly occupied by travelers as stopovers en route their journey, the duration of stay at transient hotels are very short, a day or even less.
Semi-residential Hotel
These hotels are generally patronized by people who are staying at a location while in transit to another place. The duration of stay may range from a few weeks to some months. They incorporated the feature of both transient and residential hotels.
Residential/Apartment Hotel
As the name suggests, residential hotels provide accommodation for long duration and are patronized by the people who stay for a long time. The duration of stay may range from a few months to a few years.
Extended Stay Hotel
In today’s age of downsizing, outsourcing and mobility business executive are often away from their hometowns for extended periods of time and require more than a hotel room.
These hotels are for those guests who wish to stay for long period (from few days to weeks), and cater to their long-term needs with special services, amenities, and facilities, such as full-fledged kitchens with dishes and kitchenware, separate area to wash clothes, housekeeping services, grocery services, and recreational facilities. The room rates of these hotels are determined by the length of stay.
Classification of Hotels on the Basis of Level of Services
On the basis of services offered by a hotel, they may be classified into the following categories:
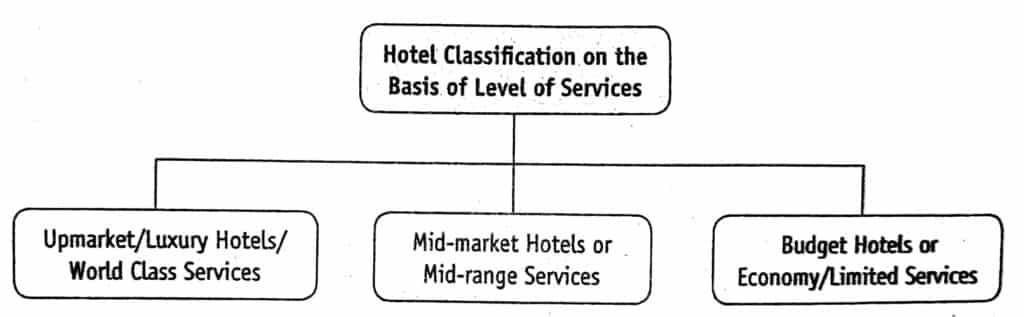
Upmarket/World Class Luxuries Hotels
Targeting the affluent segment of society, hotels in the upmarket category offer world-class products with personalized services to the higher standard. The emphasis is on excellence and class. These hotels provide upscale restaurants and lounges, exquisite décor, concierge service, opulent rooms, and abundant amenities.
The design and interior decoration of the hotel itself reflects the standards maintained by the hotel. The guest rooms are large with exquisite decoration and furnishings.
Mid-Market/Mid-range Services Hotels
These hotels offer modest services without the frills and personalized attention of luxury hotels, and appeal to the largest segment of travelers. They may offer services such as room service, round-the-clock coffee shop, airport and railway station pick-up and drop facilities; multi-cuisine restaurant with bar.
A typical hotel offering mid-range service would be medium-sized, having roughly 150 to 300 rooms. The room rent is much lower than the upmarket hotels. These hotels are patronized by business traveler, individual traveler, and groups.
Budget/Economy Hotels
Budget hotels focus on meeting the most basic needs of guests by providing clean, comfortable, and inexpensive rooms. These are also known as economy or limited services hotels, they appeal primarily to budget-minded traveler groups.
The clientele of budget hotels may also include families with children, bus tour groups, traveling business people, vacationers, retired persons, and groups. These hotels have clean and comfortable guest rooms, a coffee shop, a multi-cuisine restaurant, in-room telephone, and channeled music and movies.
Classification on the Basis of Ownership
On the basis of ownership of a hotel, they may be classified into the following categories:
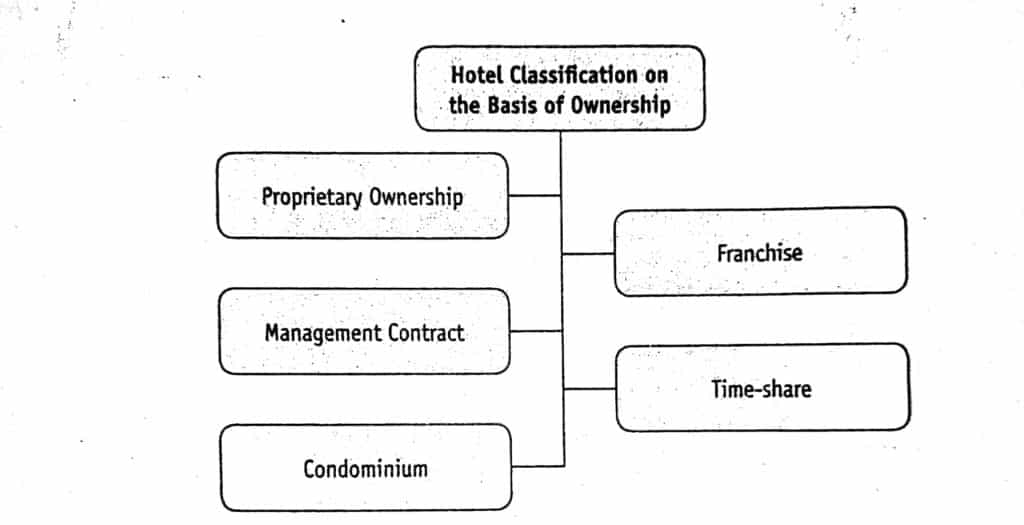
Proprietary Ownership
Proprietary ownership is the direct ownership of one or more properties by a person or company. Small lodging properties by the person or company. Small lodging properties that are owned and operated by a couple or family are common of proprietary ownership.
Franchise
Let us understand the following terminologies related to the franchise before we talk about it :
Franchise It is authorization given by a company to another company individual to sell its unique products/services and use its trademark according to the guidelines given by the former, for a specified time, and at a specified place.
Franchisor The franchisor is the company that owns the trademark, product, a business format that is being franchised.
Franchisee The franchisee is the company or the individual to whom franchise confers the right to do business under its name as per the term and condition agreed upon.
Franchising A continuing relationship in which the franchisor provides a licensed privilege to do business, plus assistance in organizing, training, merchandising, and management in return for a consideration from the franchise.
In the hospitality industry, we often come across many big chains that are operating on a franchise basis. In this kind of contract, which is mutually beneficial to both parties, the franchisor allows the franchisee to use the company’s ideal methods, trademarks, as well as the brand logo to do business.
Management Contract
Managing a hotel requires professional expertise. A new entrepreneur with little or no experience in the business may safely choose to become the franchisee of any well-established hotel chain.
There could still be a problem in operating the business because the franchisor provides a well-established image, a tested and successful operating system, training programme, marketing, advertising, and reservation system, but does not provide the cadre of an experienced manager and the employees necessary to run the business on a day to day basis.
To bridge the gap, management contract companies came into existence. These companies have the required expertise to manage hotels. They operate on the basis of management fee and the sometimes on a percentage of gross revenue.
Time-share Hotels
Time-share hotels, also referred to as vacation-interval hotels, are a new concept in the hospitality industry. As the name suggests, it entails purchasing a tourist accommodation at a popular destination for a particular time slot in a year.
The buyer can then occupy the property for the appointed time or rent the unit to other vacationers if they cannot avail the facilities. They have to make a one-time payment for the time slot and a yearly fee to cover the maintenance costs and related expenses and take a share in the profit from the income generated if they are not utilizing their time slot.
Condominium Hotels
Condominium hotels are similar to timeshare hotels, expect that condominium hotels have a single owner instead of multiple owners sharing a hotel. In a condominium hotel, the owner informs the management company when they would occupy the unit.
The management company is free to rent the unit for the remainder of the year, and this revenue goes to the owner. The owner generally pays a monthly or annual maintenance fee to the management company that takes care of the premises, including landscaping, cleaning of common areas, water, and power supply etc.
Alternative of Hotels Accommodation
Alternative accommodation can be simply defined as ‘all those types of accommodation that are available outside the formal or organized accommodation sector’. These establishments provide bed and breakfast and some basic services required by the guest at a reasonable price.
An alternative accommodation, thus, providing sleeping space and modest food for its users. There are certain properties that cater to the needs of a large group.
The lodging houses constructed for the welfares of common travelers, such as sarais, dharmshalas, dak bungalows, circuits, houses, inspection bungalows, lodges, youth hostels, yatri niwas, and forest lodges are the example of alternative accommodation.
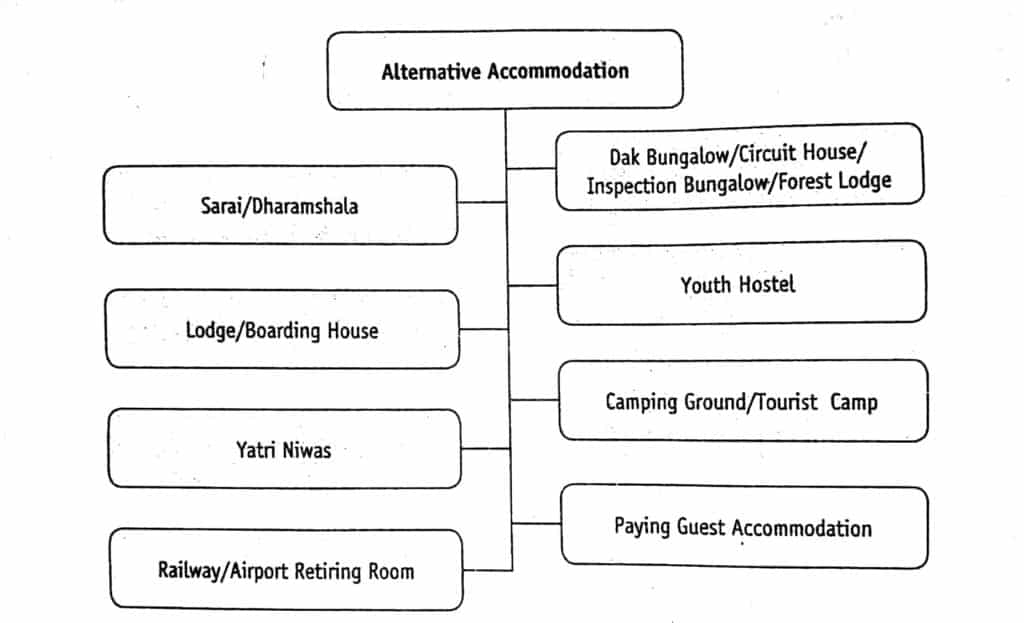
Sarai/Dharmshala
These lodging properties are mostly found at popular pilgrimage places. They are generally constructed by welfare trusts, social organizations, or even the state, and provide basic security and sleeping facilities for a nominal fee.
Dak Bungalow/Circuit House
These accommodation are situated in remote areas and at scenic locales. All these properties have an ageless charm and an old world style of hospitality as well as special cuisine, which forms a part of the attraction, apart from the low traffic. Often these are the only lodging properties in remote areas.
Lodge/Boarding House
Lodges are modest hotels situated away from the center of the city or located at a remote destination. These are self-sufficient establishments that offer standard facilities, such as clean and comfortable rooms, food and beverage (F&B) services.
Boarding houses are establishments that usually provide accommodation and meal at a specified period of time, such as weekends, or for a specified time of stay.
Youth Hostel
The youth, from rural as well as urban areas, travel for various reasons, such as education, adventure, and recreation. Youth hostels were established to cater to the youth on the move, who couldn’t afford steep hotel rents.
A youth hostel generally provides low-cost dormitory accommodation with common bathing and cafeteria facilities. They may also provide kitchens for self-catering.
Yatri Niwas
A yatri niwas provides low cost, self-service accommodation to domestic tourists in cities. The emphasis is on modest comfort and affordability. These are generally frequented by people during brief stopovers while traveling between places, or by families with modest budgets.
These properties are located at historical, cultural, and natural sites.
Camping Grounds/Tourist Camps
Camping grounds are normally located within cities in open space. They provide parking spaces along with the water, electricity, and toilets. Camps must follow certain regulation regarding the quality of services and cost and are set up by municipalities.
Railway/Airport Retiring Rooms
A retiring room is for the convenience of the transit travelers. These are situated at a major railway station and domestic and international airports. They provide resting rooms are available at reasonable rates and are often air-conditioned. Booking for the same is made through the station superintendent or the airport manager.
They are equipped with clean sanitation facilities and may include F&B facilities at a cost.
Paying Guest Accommodation
A paying guest (PG) accommodation is a non-institutional accommodation offered by individual households at various destinations. Besides tourist haven like Goa, this kind of accommodation is becoming popular in large metropolitan cities among outstation students and the employed youth migrants from other towns.
Guests normally pay for accommodation, while the rules for F&B services may differ from host to host.
Hotel Traffic Plans
The various traffic patterns followed by hotels have come to be identified with the area where such patterns originated. Hotels charge their guest according to European, Continental, American, Bed and Breakfast meal plans, etc. We shall briefly discuss these plans. These are followed as:
European Plan
The tariff consists of room rate only. All other expenses would be paid by the guest as per the actual use of consumption.
Continental Plan
The room tariff includes continental breakfast, along with the room rent. Continental breakfast includes a choice of fresh or canned juices; bread like the croissant, toast, brioche, etc. with butter or preserves like jam, jellies, and marmalade; beverage like tea or coffee, with or without milk.
American Plan
It is also known as en-pension or full board. The tariff includes all meals (breakfast, lunch, and dinner) along with the room rent. The menu for the food and beverage is fixed.
Modified American Plan
It is also known as demi-pension or half board. The tariff consists of breakfast and one major meal (lunch or dinner) along with the room rent.
Bed & Breakfast (B&B) or Bermuda Plan
The room traffic includes American breakfast along with room rent. American breakfast includes most or all of the following: two eggs (fried or poached), sliced bacon or sausage, sliced bread or toast with jam/jelly/butter, pancakes with syrup, cornflakes or other cereal, coffee/tea, and orange/grapefruit juice.
Types of Hotel Guest Rooms
A hotel sells a combination of accommodation, food, drinks, and other services and facilities to its guests. The main accommodation product is the room, which is among the principal source for the hotel. Other facilities and benefits such as ambiance, décor, in-room amenities, and security, are the add-on that plays a significant role in the pricing of the services.
In order to suit the profile and pocket of various guests, hotels offer different types of rooms that cater to the specific need of guests. The rooms may be categorized on the basis of the room size, layout, view, interior decoration, and services offered. The various types of rooms offered by a hotel are as follows:
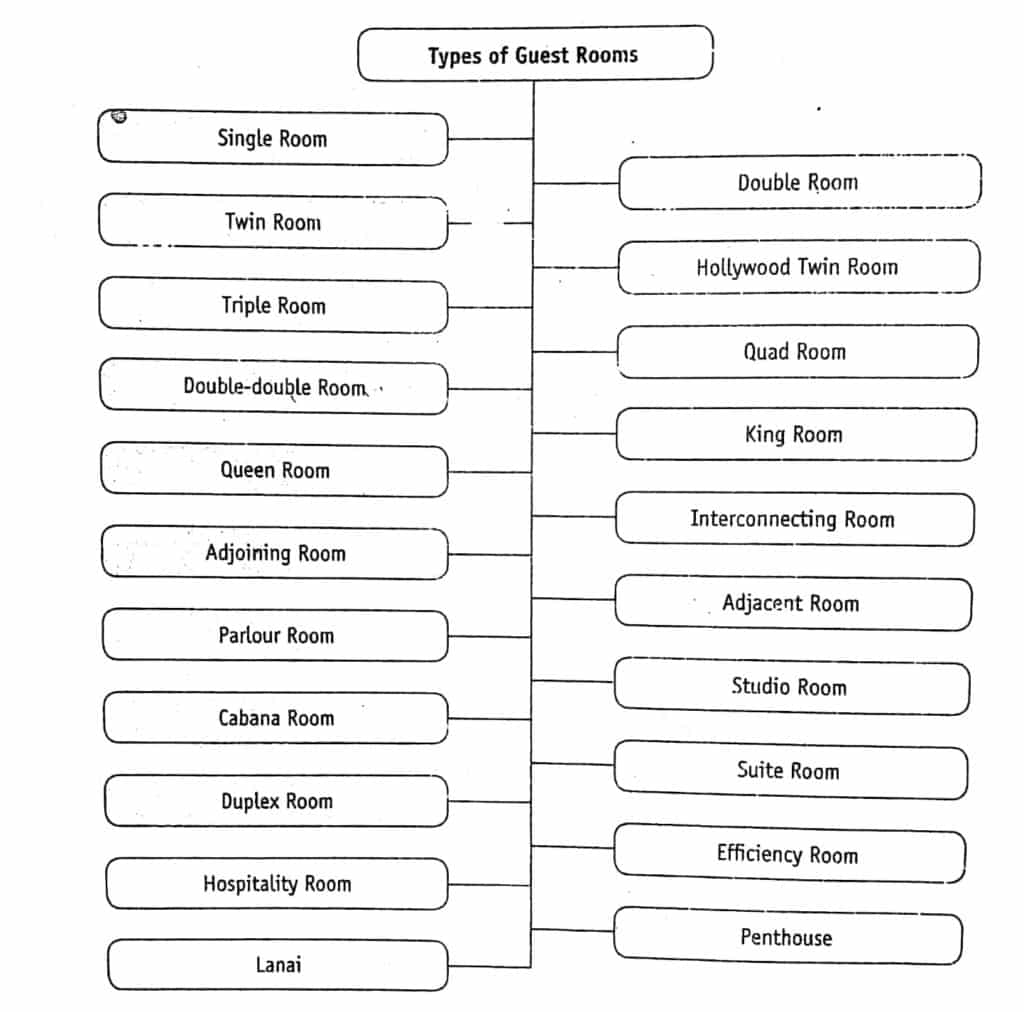
Single Room
A single room has one single bed for single occupancy. An additional bed (called extra bed) may be added to this room on the request of a guest and charged accordingly. The size of the bed is normal 3 feet by 6 feet. However, the concept of single rooms is vanishing nowadays. Mostly, hotels have twin or double rooms and charge for the single room, if occupied by one person.
Twin Room
A twin room has two single beds for double occupancy. An extra bed may be added to this room on the request of the guest and charged accordingly. The bed size is normally 3 feet by 6 feet. These rooms are suitable for sharing accommodation among a group or delegates meeting.
Double Room
A double room has one double bed for double occupancy. An extra bed may be added to this room on the request of a guest and charged accordingly. The size of the double bed is generally 4.5 feet by 6 feet.
Triple Room
A triple room has three separate single beds and can be occupied by three guests. This type of room is suitable for groups and delegates of meetings and conferences.
Quad Room
A quad room has four separate single beds and can accommodate four persons together in the same room.
Hollywood Twin Room
A Hollywood twin room has two single beds with a common headboard. This type of room is generally occupied by two guests.
Double-Double Room
A double-double room has two double beds and normally preferred by a family or group as it can accommodate four persons together.
King Room
A king room has a king-size bed. The size of the bed is 6 feet by 6 feet. An extra bed may be added to this room on the request of a guest and charged accordingly.
Queen Room
A queen room has a queen-size bed. The size of the bed is 5 feet by 6 feet. An extra bed may be added to this room on the request of a guest and charged accordingly.
Interconnecting Room
Interconnected rooms have a common wall and a door that connects the two rooms. This allows guests to access any of the two rooms without passing through a public area. This type of room is ideal for families and crew members.
Adjoining Room
Adjoining rooms share a wall with another hotel room but are not connected by the doors. For eg. Room no. 201 and 202, 203, and 204, 205 are adjoining as each pair of rooms shares a common wall.
Adjacent Room
An adjacent room is very close to another room but does not share a common wall with it.
Parlor Room
A parlor room has a living room without a bed and may have a sofa and chairs for sitting. It is generally not used as a bedroom.
Studio Room
A studio room has a bed and a sofa-cum-bed and is generally used as a living room.
Cabana
A cabana is situated away from the main hotel building, in the vicinity of a swimming pool or sea beach. It may not have beds and is generally used as a changing room and not as a bedroom.
Suite
A suite comprises more than one room; occasionally, it can also be a single large room with clearly defined sleeping and sitting areas. The décor of such units is of very high standards, aimed to please the affluent guest who can afford the high traffic of the room category.
Duplex
A duplex suite comprises two rooms situated on different floors, which are connected by an internal staircase. This suite is generally used by business guests who wish to use the lower level as an office and meeting place and the upper-level room as a bedroom. This type of room is quite expensive.
Efficiency Room
An efficiency room has an attached kitchen and bathroom for guests preferring a longer duration of stay. Generally, this type of room is found on holiday and health resorts where the guest stays for a longer time.
Hospitality Room
A hospitality room is designed for hotel guests who would want to entertain their own guests outside their allotted rooms. Such rooms are generally charged on an hourly basis.
Penthouse
A penthouse is generally located on the topmost floor of hotels and has an attached open terrace or open sky space. It has very opulent décor and furnishings and is among the costliest rooms in the hotels, preferred by celebrities and major political personalities.
Lanai
A lanai has a veranda or roofed patio and is often furnished and used as a living room. It generally has a view of a garden or sea beach.
Top Leaders in Hospitality Industry
They are those persons who contribute in the hospitality industry a lot. Some famous names are following as:
Ellsworth Statler
Ellsworth Statler is a famous name in the field of hospitality as he was one of the pioneers of this industry and contributing and contributed immensely to the development of the hospitality industry through his innovative ideas, which are still applicable in the various fields of the hospitality industry.
In 1908 A.D., he opened as an innovative hotel of its own kind during that time called Buffalo Statler which had the room with some modern facilities such as attached bathrooms, telephone facilities, and restaurant facilities.
Statler also contributed a great deal towards the international marketing efforts in the field of the hospitality industry. Statler was also very popular among his employees, as he believed in the concept of the internal marketing as he used to consider his employees as internal guests.
Conrad Hilton
Conrad Hilton is also a very famous name in the field of hospitality and was one of the pioneers of the modern hotel industry. Hilton becomes a famous and successful hotelier after World War I when he brought the Mobley hotel in Texas and built the Hilton Hotels in Dallas, Texas in 1925. After the World War II, he formed the Hilton Hotels Corporation in 1946 and then he formed Hilton International Company, which had about 125 hotels under its banner.
Hilton was the first major and organized hotel chain of American hotels when Conrad Hilton purchased the Statler chain of hotels in 1954. Today Hilton Hotels are spread in most of the countries of the world and includes Conrad International, Doubletree, Red Lions Hotels, Harrison Conference Centers, Homewood Suites and Embassy Suites.
J. Willard Marriott
J.W Marriot was another pioneering name in the world of the hospitality industry. He started the Marriott Chain of Hotels and thus became a frontline leader in the field of hospitality. He was thoroughly aware of the employees/consumer relationship and tried to make sure that his employees were totally satisfied with their job and working environment.
He had a strong marketing brain and could forecast the importance of airline catering business for various airlines operations and was the first to enter in the field of hospitality. In today scenario, Marriot Corporation is one of the leading companies in the field of hospitality with an annual sale of $7.5 billion and has a variety of food and beverage service operation under his banner.
The lodging chain of Marriott includes Marriott Hotels and Resorts, Marriott Suites, Residence Inns, Courtyard Hotels and Fairfield Inns.
Ralph Hitz
Ralph Hitz was also a very popular personality in the hospitality industry. He was the head of a large hotel organization in U.S.A called the National Hotel Company. His hotel management used to receive a management fee for running day by day administration of hotel owned by real estate investors.
Hitz had excellent marketing brain, as he was the first intellectual to develop a customer database for providing the guests of hotels with personalized service leading to guest satisfaction and overall profitability of the hotels. Hitz also believed in training and motivating the employees of the hotels to give and improved services for guest satisfaction.